Financing Electricity Grids for the Energy Transition
Introduction
Electricity grids are a critical part of the energy infrastructure in the transition to a carbon neutral world. To meet the growing demand for electricity from different sectors and to accommodate an increasing share of renewable energy, electricity grids need to be expanded and modernised. This will require massive investment over the coming years.
Investments in Electricity Grids
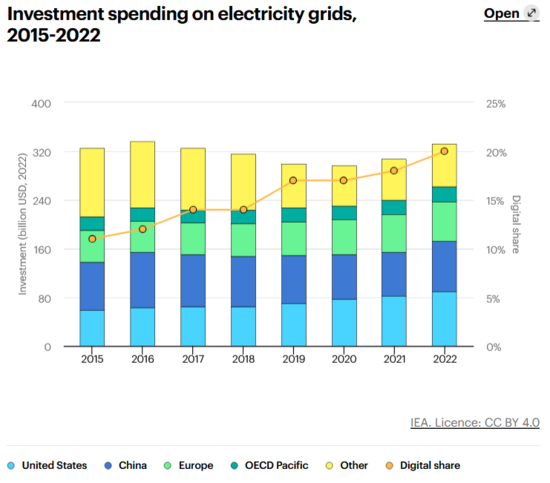
Current investment levels are around USD 300 billion per year, with a general upward trend (+8% in 2022). According to the IEA, global investment will need to almost double by 2030 to achieve net-zero emissions by 2050.[1]
The European Commission estimates that €584 billion will be needed to meet the EU's 42.5% renewables target by 2030.[2]
Financing Mechanisms for Electricity Grids
Investments in electricity grids need funding from both public and private sectors.
International Finance
Public Funding
The Role of Financial Institutions
De-risking Investments
End-User Tariffs
Further Information
- Financing and Funding Portal on energypedia
- Electricity Grids Portal on energypedia
References
- ↑ IEA, smart grids, retrieved November 2024
- ↑ European Investment Bank, Investing in grids to power the energy transition, retrieved November 2024