Tajikistan Energy Situation
| Tajikistan | |||
| |
| ||
| Capital | Dushanbe (38° 33′ 0″ N, 68° 48′ 0″ E) | ||
| Official Language(s) | Persian (Tajik) | ||
| Government | Unitary semi-presidential republic | ||
| President | Emomalii Rahmon | ||
| Prime Minister | Oqil Oqilov | ||
| Total Area |
143,100 km2 | ||
| Total Population | 7.6 million | ||
| Urban-Population | 2 million (26%) | ||
| Rural-Population | 5.6 million (74%) | ||
| Population Density | 48 Persons per km² | ||
| Average Household Size | 6.3 | ||
| GDP (nominal) | |||
| GDP per Capita | $362.00 | ||
| GNI per Capita | $ 468.00 | ||
| Currency | Somoni (TJS) | ||
| Time Zone | TJT (UTC+5) | ||
| Calling Code | +992 | ||
Geography and Climatic Conditions
Tajikistan is Central Asia's smallest country. It is landlocked and lies int the active seismic zone with frequent earthquakes. Mountains and territory over 3000m high covers 93% of its area, with the the Pamir and Alay Mountains dominating the landscape.[1]
Its climate is continental with seasonal variations. It has hot summers and mild winters and a semiarid to polar climate in Pamir Mountains
The average low and high temperatures are 8.1°C and 22.0 °C, respectively. [1]
2.9% of the land in Tajikistan is covered by forest. The forest annual rate of change (between 2005-2010) was 0% [2]
Socio-economic Situation
Tajikistan has a population of 7.6 million, the majority of which (74%), lives in rural areas. The population density is 48 Persons per km² .
Tajikistan is the poorest country in Central Asia and its economy remains fragile due to corruption, weak governance, unemployment, and seasonal power shortages. Yet recent years have seen an annual economic growth rate of 8-10%. The current GDP is ____ and GDP per capita is ___. Its economy is based on the production of hydro power, cotton, and aluminum and national income sources consist primarily of agriculture (49.8%), services (37.4%), and industry (12.8%). [1]
More than 40% of the populations lives under the poverty line of 2 USD/day.
National Energy Situation
Tajikistan has enormous hydro power potential as it possesses 4% of the world's hydro power resources and 53% of Central Asia's resources. Yet these resources remain to be sufficiently developed. About 90 % of electricity generating capacity is hydroelectric, but only an estimated 5% of its potential is in use.
The country faces an energy deficit of 3.0 to 3.5 GWh, resulting in regular blackouts from October to April.
Primary energy shares in 2008 consisted of the following: 21.6% oil, 18.3% gas, 56.4% hydro, and coal 3.7%.
The electrification rate is 85.4%[3] and electricity generation was 17,00GWh
Prices vary but people typically pay 1.5 US cents/kWh.
Potential for Renewable Energies
Electricity prices are very low due to low prime costs for the large hydro plants. Thus, alternative ways to generate electricity have been limited.
Since Tajikistan's rivers have great hydropower potential, the government has focused on attracting investments for projects for internal use and electricity exports. [4]
Stability
Type your text here
Energy Consumption
National Level
Electricity
Household Level
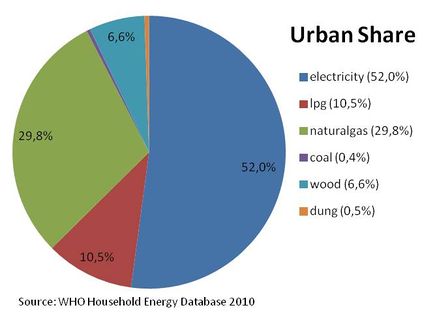
Share of energy types on cooking energy in urban areas of Tajikistan.[5]
Share of energy types on cooking energy in urban areas of Tajikistan.[5]
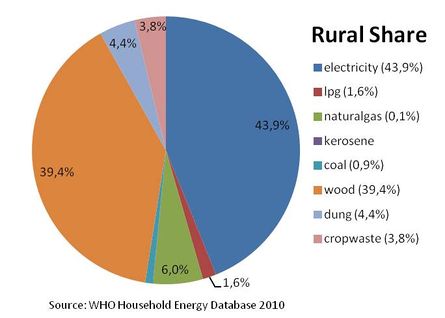
Percentage of population using solid fuels (charcoal, coal, cropwaste, dung and wood) as cooking energy.
National: 21.5%, urban:<5%, rural: 34.5% [5]
Solid Fuel Use Impact on Health
Total annual deaths attributable to solid fuel use: 1600 persons
Percentage of national burden of diseases attributable to solid fuel use: 3.5%[6]
Access Rate
Electrification Rate
National: 85.4% [7]
Renewable Energies
Application
Hydro-power is the only RE source for electricity production on national level, whose input is documented. [8]
Potentials
Solar Energy
Type your text here
Wind Energy
Type your text here
Biomass
Type your text here
Biogas
Type your text here
Hydro Power
Type your text here
Other renewable Sources
Type your text here
Key problems of the energy sector
Type your text here
Policy framework, laws and regulations
Type your text here
General Energy policy, Energy strategy
Type your text here
Important Laws and regulations
Type your text here
Specific strategies (Biomass, renewable energies, rural electrification, energy access strategy etc.)
Type your text here
Institutional set up in the energy sector
Type your text here
Governmental institutions Private sector (enterprises, NGOs)
Type your text here
Activities of other donors, activities of NGOs
Type your text here
Existing projects
Type your text here
Publications
Type your text here
External links
References
- ↑ 1.0 1.1 1.2 CIA - The World Factbook
- ↑ FAO (2011): The State of the World's Forest
- ↑ http://www.ngdc.noaa.gov/dmsp/pubs/Elvidge_WINTD_20091022.pdf
- ↑ INOGATE Energy Portal
- ↑ 5.0 5.1 5.2 WHO 2010: WHO Household Energy Database
- ↑ WHO (2006): Fuel for Life - Household Energy and Health
- ↑ http://www.ngdc.noaa.gov/dmsp/pubs/Elvidge_WINTD_20091022.pdf
- ↑ http://www.iea.org/stats/renewdata.asp?COUNTRY_CODE=KG