Wind Turbine Technology
Wind turbine control concepts
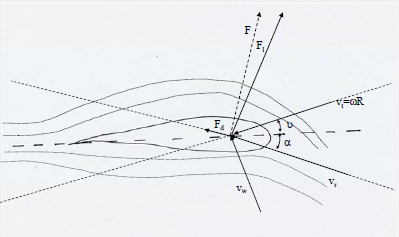
Aerodynamics
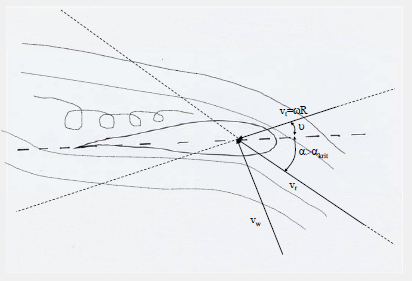
Stall
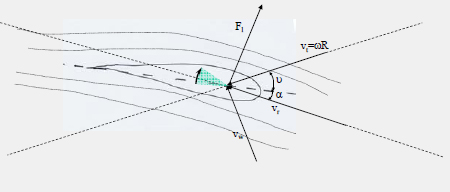
Stall Control:
– Passive Stall:
Power of the wind turbine is limited by the aerodynamic characteristics
of the turbine.
– Active stall:
Power of the wind turbine is limited additionally by decreasing the pitch
angle (increasing the inflow angle ).
Pitch
Pitch Control:
– Power of the wind turbine is limited by increasing the pitch angle
(decreasing the inflow angle )
Wind turbine operation
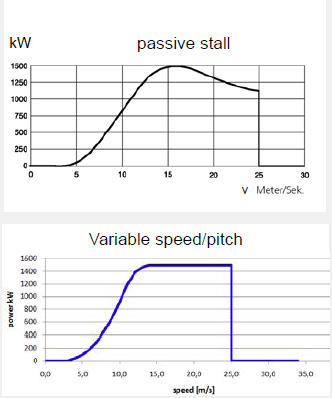
Operation of Fix Speed Wind Turbine (passive stall)
• Start up (with open breaker) if wind speed > cut-in wind speed
• Close breaker
• Operation at constant blade angle over the whole wind speed range
• In case of large wind speeds: Power limited by aerodynamic profile.
Operation of Variable Speed Wind-Turbines
Start up (with open breaker) if wind speed > cut-in wind speed
• Close breaker
• Below rated wind-speed
– Maximum power coefficient (Max. Power Tracking)
– Evt: Speed Limitation
• Above rated wind-speed:
– P=Pr
ated (Limited by power electronics converter)
– Pitching
• Advantages of variable speed operation:
– Lower cut-in wind speeds
– Higher efficiency, especially at low wind speeds
– Lower power variations (compared to fixed speed turbines)
• Disadvantage: More expensive!