Impact of Taxes on Solar Photovoltaic in India
Overview
This articles is based on the publication, "India's Energy Transition: The Impact of the Goods and Services Tax on Solar Photovoltaic and Coal Power Costs", by the Global Subsidies Initiative (GSI) of the International Institute for Sustainable Development (IISD) and the Council on Energy, Environment and Water (CEEW). It summarizes the impact on Solar PV power plants after the newly implemented Goods and Service Tax (GST).
Goods and Service Tax (GST)
On July 1, 2017, India implemented the Goods and Service Tax on all products including the energy sector. GST simplified the Indian tax system by superseding the three core taxes :the Central Goods & Services Tax (CGST), the State Goods & Services Tax (SGST) and the Integrated Goods & Services IGST (IGST). to the energy subsidies from FY2014 to FY2017
For applying GST on solar PV, 70 percent of the gross value of the contract will be considered as supply of good and have a GST of 5% while the remaining 30% will be considered as supply of service and will attract 18 percent GST.
Impact of GST on Subsidy for Solar PV
According to the publication, GST will result in a decrease of 15.6 per cent and 16 per cent in the total tax subsidy for solar PV and coal thermal power, respectively, after implementation of GST. Although the decrease is relatively similar for both the technologies, solar receives half the subsidies that coal receives.
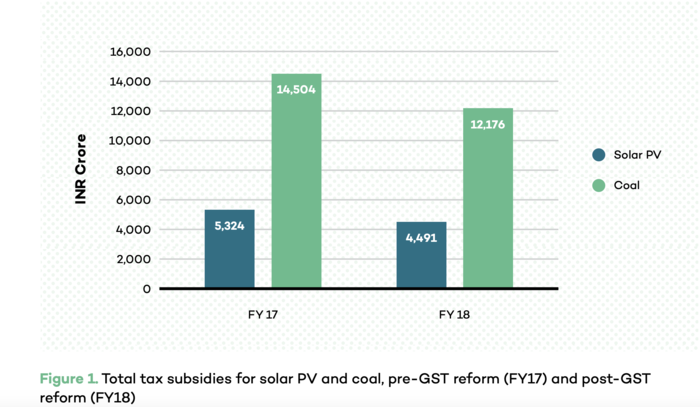
Impact on Levelized Cost of Electricity (LCOE) for Solar PV
LCOE is a metric for measuring the cost of electricity generation during the lifetime of an energy source. For calculating LCOE, the lifetime cost of the energy source (includes capital costs, O&M, performance and fuel costs) is divided by the energy produced. It helps to compared between different technology. [1]
The author calculated the impact of LCOE on a 200 MW plant solar park project adn found that after GST, after GST the LCOE increased by 5.8 as compared to pre-GST. 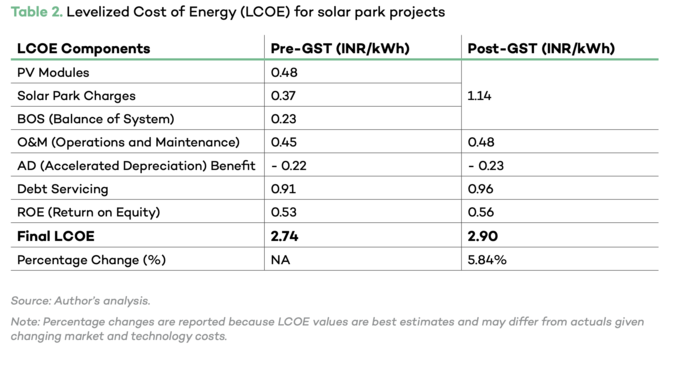
Other Taxes



















