Solar Water Heater
Overview
Obtaining hot water is energy intensive. In developing countries, households often spend a large portion of their energy budget on heating water. Solar thermal water heaters are a sustainable solution for poor households as they allow the barrier of high upfront costs to be overcome.[[1]
The technology of solar thermal water heaters is present worldwide and significant deployments are already occurring in emerging economies and developing countries. Regions that do not experience freezing temperatures can use the simplest and most cost-effective kinds of this technology.[2] In fact, more than 90% of systems worldwide are based on the thermosiphon principle (for a definition see below regarding passive systems).[3]
| A SWH with a water tank in Bolivia. (Picture: GIZ Energising Development Bolivia) |
The Technology
Solar water heating (SWH) systems are typically composed of:
- Solar thermal collectors (flat plate or evacuated tube)
- A storage tank
- A circulation loop.
State of the art solar water heaters incorporate features such as: selective surface absorbers, anti-reflective glazing, well-designed collector arrays, and efficient storage systems thereby achieving operation efficiencies of the order of 35 to 40%. Even the simplest types allow households to have convenient access to hot water.[4].
Active vs. Passive Systems
SWH can be either active system or pasive systems:
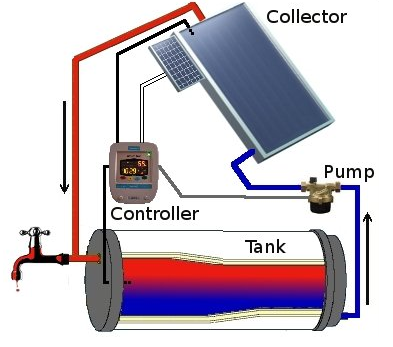
| Active system: collector, tank, pipe and controller[5] |
- Active systems use either pumps to circulate water or a heat transfer fluid which utilizes electrical components (e.g. a controller). There are two types of active solar water-heating systems:
- Direct-circulation systems use pumps to circulate pressurized potable water directly through the collectors. These systems are appropriate in areas that do not freeze for long periods and do not have hard or acidic water.
- Indirect-circulation systems pump heat-transfer fluids through collectors. Heat exchangers transfer the heat from the fluid to the potable water. Some indirect systems have "overheat protection" which is a method of protecting the collector and the glycol fluid from becoming super-heated when the load is low and the intensity of incoming solar radiation is high.
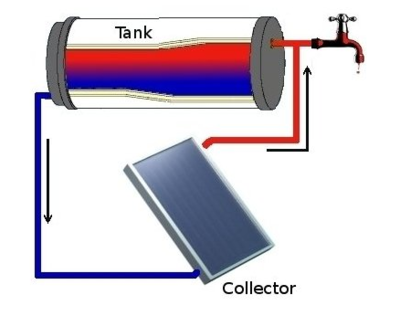
| Passive system: collector and tank[5] |
- Passive systems transfer and circulate heat naturally. Passive solar water heaters rely on gravity and the tendency for water to naturally circulate as it is heated. Because they contain no electrical components, passive systems are generally more reliable, easier to maintain, and possibly have a longer work-life than active systems. The two common types of passive systems are described below:
- Integral-collector storage systems or batch systems consist of a tank that is directly heated by sunlight. These are the oldest and simplest solar water heater designs and are good for households with significant daytime and evening hot-water needs. However, they do not work well in households with predominantly morning usage because they lose most of the collected energy overnight. These solar collectors are suited for areas where temperatures rarely go below freezing.
- Thermosyphon systems are an economical and reliable choice. These systems rely on the natural convection of warm water rising to circulate water through the collectors and to a storage tank located above the collector. As water in the solar collector heats, it becomes lighter and rises naturally into the tank above. Meanwhile, the cooler water flows down the pipes to the bottom of the collector, thereby enhancing the circulation. Indirect Thermosiphon systems use a glycol fluid in the collector loop as a heating medium.[6]
Most solar thermal systems installed in developing countries are thermosiphon systems.
Collectors
Flat Plate Collector
A flat plate is the most common type of solar thermal collector and is typically used as a solar hot water panel to generate hot water. A weatherproofed, insulated box containing a black metal absorber sheet with built-in pipes is placed in the path of sunlight. They can be deployed on the roof of buildings or on the ground. Solar energy heats the water in the pipes causing it to circulate through the system by natural convection. The water is then usually passed to a storage tank located above the collector.
There are many flat-plate collector designs but generally all consist of:
- a flat-plate absorber which intercepts and absorbs the solar energy,
- a transparent cover that allows solar energy to pass through but reduces heat loss from the absorber,
- a heat-transport fluid (air, antifreeze or water) flowing through tubes to remove heat from the absorber and
- a heat insulating backing.
One flat plate collector is designed to be evacuated, therefore preventing heat loss. The absorber can be made from a wide range of materials, including: copper, stainless steel, galvanised steel, aluminium and plastics. When choosing an absorber material it is important to ensure that it is compatible, from the point of view of corrosion, with the other components in the system and with the heat transfer fluid used. The absorber must also be able to withstand the highest temperature that it might reach on a sunny day when no fluid is flowing in the collector (known as the stagnation temperature).
The fluid passageways of the absorber may consist of tubes bonded to an absorbing plate or may form an integral part of the absorber. Experience has shown that the simple mechanical clamping of tubes to an absorber plate is likely to result in an absorber with a poor efficiency. A good thermal bond, such as a braze, weld or high temperature solder, is required for tube and plate designs as it ensures efficient heat transfer from the absorbing surface into the fluid.
Matt black paints are commonly used for absorber surfaces because they are relatively cheap, simple to apply and may be easily repaired. Paints, however, have the disadvantage that they are usually strong emitters of thermal radiation (infrared) and at a high temperature this results in significant heat losses from the front of the collector. Heat losses from the collector can be substantially reduced by the use of absorber coatings known as 'selective surfaces'. These surfaces may be applied by electroplating or by dipping a metal absorber in appropriate chemicals to produce a thin semi-conducting film over the surface. The thin film will be transparent to solar radiation while simultaneously appearing opaque to thermal radiation. However, these surfaces cannot be produced or applied easily.
Flat-plate collectors usually have a transparent cover made of glass or plastic. The cover is required to reduce heat losses from the front of the collector and to protect the absorber and the insulation from the weather. Most covers mimic a greenhouse environment. They permit solar radiation to pass into the collector while also absorbing the thermal radiation emitted by the hot absorber.
At night it is possible for the collector to lose heat by radiation resulting in the circulation being reversed and the water cooling. This can be overcome by use of a suitable non-return valve. However, there is a danger with solar collectors when used under clear night conditions (e.g. in arid and semi-arid regions) that they can actually freeze even when the ambient temperature is above freezing point. In such conditions it may be necessary to have a primary circuit through the collector filled with antifreeze and a separate indirect hot water cylinder where the water from the collector passes through a copper coil to heat the main water supply. This problem will only apply in certain desert regions during the cold season or at high altitudes in the tropics and sub-tropics.
Evacuated Tube Collector
Evacuated-tube solar collectors tend to be more efficient but also more expensive. They are used more frequently for commercial applications in the U.S.A. A collector is made up of several pipes in parallel rows that are connected at the top. The tubes consist of a vacuum with a pipe running through the middle containing the working fluid. The water moves up and down and along through the series of pipes to exit the system at a significantly higher temperature. The heat loss is significantly reduced thanks to high negative pressure in the glass tubes. They can be deployed nearly horizontally on flat roofs.[7][8]
Installation and Maintenance
Basic rules for a good installation include: a preliminary study and a needs assessment to determine the best size for the specific installation and a location that is well-exposed to the sun with no shading (from nearby buildings, vegetation, etc.).[9]
The following data is required to design, size and select a solar water heating system:: daily hot water requirement (litres/day), average insolation (kWh/m2 day), water quality and storage requirements[4].
Find more technical details on SWH: http://www.geni.org/globalenergy/research/solar-water-heaters/solar-water-heater.pdf
Solar thermal systems are relatively maintenance free and only require an inspection of the piping for leaks and the cleaning of the collectors on an occasional basis. In some regions, it may also be necessary to inspect the transfer fluid for freeze protection and to remove the build-up of lime scale that chokes the collector and tank recirculating pipes over time.
Advantages and Disadvantages of Thermosiphon SWH
| Advantages |
Disadvantages |
|---|---|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Solar water heater thermosiphon in Peru:
Costs
Solar water heating systems are usually more expensive than conventional water heating systems when electricity is available. However, a solar water heater can save money in the long run.
How much money can be saved depends on:
- the amount of hot water needed,
- the performance of the system,
- the geographic location and solar resource availability ,
- available public financing and incentives,
- the cost of fuels (e.g. natural gas, oil, electricity, biomass) otherwise used for heating water,
- the cost of the fuel used for the backup water heating system (if existing).[10]
SWH are very efficient, and can reduce either the electricity needs or reduce the costs for heating water by nearly 75% annually.[9]
Initial costs for a solar thermal system vary among countries and depend on the quality of the solar collector, the labour costs of installation, and also on the climate conditions in which the solar thermal systems works. Initial costs depend on the level of governmental support for SWH as well as the development of local industries. Quality of the solar collector: Lower quality products are assumed to have a life expectancy of only half of higher quality products.[11]
See details for different system sizes within the chapter about households, social institutions and productive use.
Target Groups for SWH
SWHs are employed in: residential, public buildings and institutions, commercial and industrial buildings and in industrial processes (drying, pre-heating boiler feed water, cleaning, etc. - see examples for potential on solar thermal applications in industries in India) for the provision of hot water, heat and cooling.
Energy demand for hot water is often difficult to predict as hot water demand is influenced by factors such as: user habits, number and efficiency of appliances and the required water temperature.[6]
The current commercial market for SWH is predominantly: households (mostly high income), hospitals, commercial establishments and tourist facilities. Therefore, this article distinguishes between Solar Water Heating for household uses, for: social institutions, like schools or hospitals and for productive uses in commercial enterprises.
SWH for Households
Household interests differ depending on their demand, the availability of different system sizes and what they can afford to pay. Relevant questions are, for example, how big must the system be for a family? How many liters of water can usually be heated? How much are the initial costs? What are the alterative costs for biomass heating or other options? What is the payback time for the SWH?
The system size depends on the number of family members and on the climate: In hotter climates, thermosiphon SWH have often only a smaller collector area of around 2-4 m² and a 100-300 litre storage tank. In China, for example, thermosiphon SWH with an evacuated tube collector of around 2 m² have a hot water storage tank of around 120-200 litres.[12] A 300-liter system is typically suited for family of 4-6 persons and will provide up to 1000 kWh of electricity annually.[13]
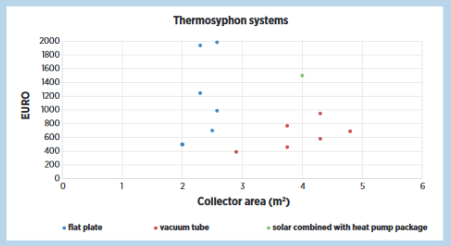
Costs for SWH largely vary among countries: usually prices for SHW are between USD 250-2,500/kW. However, in some developing countries prices could be less than half of this. The figure below shows that the costs for a SWH do not only depend on the type of SWH (blue dots: flat plate collector, red dots: evacuated tube collector, or green dots: active system with a pump) or the collector area, but also on the costs for specific applications of each system (e.g. different materials for tanks, insulation, piping) or other characteristics like warranty (e.g., 5 or 10 years).[12]
Figure: Prices for final customers for internationally traded thermosiphon systems (2014).[12]
Most solar thermal systems cost between USD 2,000 and 4,500 to install. This is a high up-front costs, however, this is often cost competitive considering the total energy costs over the entire lifetime of the system compared to electricity-based (generators) or biomass heated water.[14]
In China, initial investment costs for a direct thermosiphon systems for households with average collector size of 4 m² (2.8 kW th ) range from 100 to 250 USD/kW th (90 to 225 EUR/kW th ) with an energy cost ranging from 2 to 5 USD cents/kWh th (1.8 to 4.5 EUR cents/kWh th ). In the Mediterranean region, the average cost for a open-loop, pressure-less thermosiphon systems (180 litre hot water, 70 litre feeding tank) is around 920 USD (830 EUR).[15]
In Rwanda, households can save up to 70% of their electrical bills after switching to a solar SWH. Depending on the geographical areas, water consumption patterns and type of system selected, a payback period of 3-5 years is common. After that time, the SWH produces hot water without regular bills.[16] Because of the high upfront costs, the solaRwanda programme offers a subsidy for quality approved systems.
Switching from electrical to solar water heating systems would lead to yearly energy savings of about 930kWh in a local Native American community of California. Using the SWH for showering and other daily hot water uses, the payback period is only 7 years.[17]
Low temperature flat-plate solar collectors typically cost 21 US $ per square metre (0,0021 US $ /cm²). Medium to high temperature collectors generally cost around 200 US $ per square metre. Flat plate collectors are sized at approximately 0,1 square metre (929 cm²) per gallon (3,79 l ) of daily hot water use or 245 cm² per l of hot water. A complete system installed costs around 14 US $/l or 2000 US $ per 150 l.[18]
Solar Water Heating in Social Institutions
Solar Water Heaters are used in different social institutions, wherever there is a substantial use of domestic hot water. These include schools, hospitals, swimming pools and sport facilities, dormitories, retirement homes, etc. Depending on requirements, the sizes of SWH installations vary widely. Small systems have a collector size of 10 m² (7 kWth); larger systems up to 500m² (350 kWth).[19]
System requirements depends on:
- Quantity of hot water
- timeframe (when it is needed)
- desired temperature
Social institutions need to assess the system sizes that suits them best regarding their needs (e.g.: how big must the system be for a hospital, for a school? How many liters of water can be heated usually?) and their possible financial means. (e.g. What are the initial costs? Is there a financing option available? What is the payback time?)
Potential savings and the respective energy costs depend on three main aspects:
- initial cost of the system
- lifetime of the system
- system performance
These factors depend on the location (affecting climate, insulation, taxes, cost of living, etc.) and quality of the system (affecting performance, lifetime and cost). This can vary significantly from country to country, as well as system to system.
In contrast to households systems that use thermosiphon passive systems, SWH for social institutions are most commonly using mostly active, pumped indirect systems. Initial investment costs range between 850 to 2400 USD/kWth (765 to 2160 EUR/kWth) with running energy costs between 10 and 29.5 USD cents/kWhth (9.5 to 26.6 EUR cents/kWhth) in central and northern Europe.[19]
Lessons learnt from a project in Bolivia Energía para infraestructura social (energy for social infrastructure):
- Communities faced technical difficulties to provide portable water and infrastructure at the beginning, overcame them and improved the situation and learning environment for their students.
- The participation of teachers and also parents in teaching about hot water usage was of utmost importance for the good use and sustainability of the solar thermal systems.
- Communities that installed thermal solar systems in health points supported the improvements of the hygienic and health situations of the personal and the patients.[20]
Find more information for social institutions:
- Global Solar Water Heating Market Transformation and Strengthening Initiative (GSWH Project. ‘Solar Heating and Cooling Application Factsheet: Domestic Water Heaters for Social Amenities’, 2015. http://www.solarthermalworld.org/sites/gstec/files/story/2015-10-14/application_factsheet_swh_social_amenities.pdf.
Productive Use of Solar Water Heating
Heating water is a small but essential element of a wide range of production processes in agricultural, industrial and service sectors. Hot water is needed, for example, in restaurants for cooking and cleaning, in industrial processes for dissolving substances or cleaning equipment (e.g. dairies), in hotels for hot showers, etc. Productive use applications of solar water heaters arise in various industries, notably in the food service and hotel industries. Reliable and sufficient availability of hot water usually implies higher and cleaner service quality, which allows restaurants and hotels to attract more clients or increase price.[21]
Companies consider the following aspects before acquiring a SWH:
- System sizes (e.g.: how big must the system be for a small Hotel? How many liters of water can be heated usually?)
- Costs / payback time
Locally produced solar water heaters are of low costs for construction and the devices are simple to maintain and to repair. In comparison, the investments for industrial produced solar water heaters are often higher, but these show often good efficiency values.[21]
In Tunisia, the programme PROsol has provided SWH to 450 companies in the tertiary sector (hotels, swimming pools, hammams, etc.) via loans. It grants five years to pay back the loan through their monthly STEG electricity bill, which is a key success factor of the financial scheme, because it is a fairly reliable way of refinancing the thousands of loans.[22][23]
|
Example: Hotel in Peru The Colca River Hotel in Chivay, capital of Caylloma province in the department of Arequipa installed a SWH on their roof. “The water heater works perfectly. We installed it on the roof and all went well. We have 18 rooms, all with hot water, because from the beginning we had decided to have hot water. If we are working with tourism, we have to provide hot water. There are over 100 hotels in Chivay, for all tastes and prices, and most already have hot water”, says Israel Huaraya, the owner. They opted for the largest heater, which is 650 liters to be able to offer hot water even to large groups with up to 40 people. |
Global Market Trends for Solar Water Heaters
The use of solar energy to generate heat is a tried and tested technology and has been used for decades.[24]
Some countries have a higher degree of market penetration because the external factors are favourable:
- Usually energy cost is high to extremely high (USD 0.20 to 0 .60 per kWh th),
- Solar irradiance is excellent (H global- horiz > 4.5 kWh/m 2 -day), and
- Government provides support (e.g. subsidies to consumers or manufacturers, mandates, technology promotion).[25]
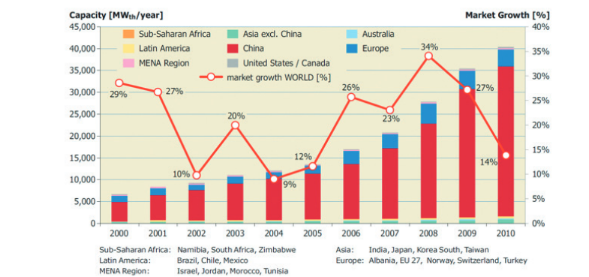
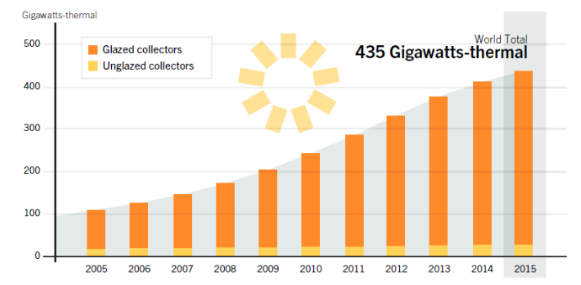
For example, in Cyprus and Israel where SWH have been mandated since the 1980s, market penetration today is at 90% in residential homes. However, the largest market is in China with the biggest share of newly installed capacity during the past years (around 80% of globally new installed capacity).[12] The markets in Sub-Sarhan Africa, Latin America, the MENA region and other Asia (excl. China) are comparable small. See figure below.
Figure: World market for SWH of flat plate and evacuated tube collectors from 2000 to 2010.[26]
Because many countries have opted for policies and financial instruments to make SWH more affordable to households, social institutions and companies, globally adoption increases on average by 25% annually during the 2000-2010 (with a lower rate due to the economic crises after 2009). Markets in Europe and China are contracting, in 2015, global SWH market only rose by 6%.[26]
The global capacity of SWH is 435 GWth in 2015.[27]
The highest capacity is installed in the following countries: China, Turkey, Brazil, India and the United States. While China and Europe experiences slower market development than in the past, Denmark, Israel, Mexico, Poland and Turkey reported significant growth in 2015, according to the Global Status Report 2016 by REN21. [27]
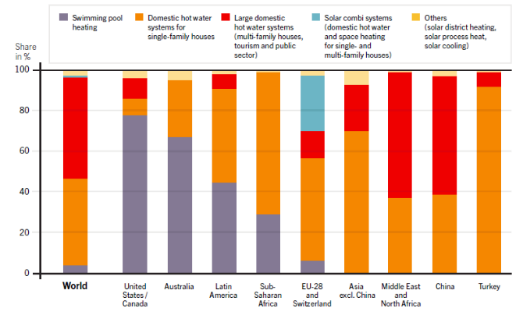
Worldwide, SWH applications differ. Globally, around half of the installed capacity is for larger domestic SWH (red bars) and the other half for smaller SWH (orange bars), with swimming pool heating (purple bars) and sophisticated SWH-combi systems (blue bars) playing only a minor role. See Figure below.
- In Latin America, smaller domestic SWH have the largest share, followed by swimming pool heating. Institutional and commercial use also plays a role.
- In Sub-Saharan Africa, majority (two thirds) are smaller systems, with also swimming pool heating of around 30% of newly installed capacity.
- Swimming pool heating does not play a role in the Middle East, North Africa and Asia. IN Asia and Middle East + North Africa, around 60% of newly installed capacity are larger SWH for institutions, while in other Asian countries (except China), around 70% are smaller SWH.
Figure: SWH applications for newly installed capacity by region, 2014.[27]
Market Barriers and Limitations
Barriers that prevent faster dissemination of SWHs are the following:
- Economic/Financial Barriers
- Relative high upfront costs of SWH is a major limitation in their uptake. See costs
- Demand side and social barriers
oLack of awareness at end-user level
Pervasive inertia on the part of most residential users to switch from conventional heating and cooling systems that provide reliable supply
- Supply side and technical barriers:
Lack of skills of installers
Water quality: Solar water heaters require clean, non-hard water for long term operation. Hard or dirty water leads to blockage and corrosion of pipes and storage tanks. Closed circuit systems are recommended where water is hard.
Quality of housing: Rooftops need to be strong enough for heavy water tanks and collectors.
Installation, Commissioning and Maintenance: Improper installation and commissioning and maintenance of SWHs are the leading causes of system failures. Lack of local manufacturing,
Lack of knowledge and SWH capabilities among architects and other decision makers within the construction and energy industries.
- Institutional & Legislative Barriers
Lack of appropriate regulatory frameworks to guarantee that SWH meet the technical requirements to ensure appropriate and reliable operation
Lacking Standards, and quality control: with increasing local manufacturing as well as international trade of SWH, international performance standards for SWH will be important to ensure continued deployment.
- Research & Development Challenges
Impacts and Benefits of Solar Water Heaters
Solar water heaters have serval impacts and benefits, especially in developing countries.
There are economic, political and benefits environmental:[15][28][29]
- Potential savings in energy costs for households, social institutions and companies
- Potential savings in energy generation costs for utilities: 100 SWH with 100 litres capacity save 1 MW during peak load. All 100 million electric water heaters of the USA replaced by Solar water heaters would reduce the peak load by about 100 GW[26].
- Creation of local jobs related to the manufacturing, commercialization, installation and maintenance of solar thermal systems
- Reduction of fuel consumption: a 100 litres SWH can save up to 1500 units of electricity annually.
- Possibility of improving energy security by reducing energy imports
- Reduction of CO2 emissions: a 100 litres SWH can prevent 1.5 tCO2/year or around 350 kg of CO2 can be saved by a SWH system with 4 m² (2.8 kWth) household size. Larger systems with a collector of 20 m² (14 kWth) could even save around 1.75 Mt CO2.
Political environment for SWH
Standards and Quality Aspects
Policies
Actors in the Field of SWH
Companies
Manufacturing SWH
Technology Providers
Research Institutes
National and International Organisations, NGOs
Further information
- Solar portal on energypedia
- All on energypedia.
- Technical Brief: Solar Water Heating by Amy Punter. This publication by Practical Action explains how solar energy may be used to heat water and how the technology works. http://practicalaction.org/solar-water-heating
- Construction of Solar Collectors for Warm Water – Practical guide by Regina Drexel and Rostom Gamisonia. This brochure by Women in Europe for a Common Future shows how to use the energy from the sun for heating water, how to construct a solar water heater and gives an overview of other solar collector models. of_solar_collectors.pdf http://www.wecf.eu/download/2010/WECF_Construction_ of_solar_collectors.pdf
- Solar Water Heater with Thermosyphon Circulation by Bernd Sitzmann. This publication describes briefly the advantages and engineering aspects of solar water heaters with thermasyphon circulation. http://www.gate-international.org/documents/techbriefs/webdocs/pdfs/e021e_2003.pdf
- Guidelines for Fabrication of serpentine solar water heaters by Ben Dana. Practical Action, 2009. http://answers.practicalaction.org/our-resources/item/serpentine-solar-water-heating-guidelines-for-fabrication
- Two very comprehensive studies on the Solar Heating and Cooling Sector were published in early June 2016: REN21’s the Renewables 2016 Global Status Report (GSR2016) from REN21 and Solar Heat Worldwide from the IEA Solar Heating and Cooling programme (IEA SHC). This webinar will highlight the key data and findings of these two studies looking at new installations, prospering applications, market barriers, industry trends, costs of solar heat and jobs. http://www.solarthermalworld.org/content/webinar-global-view-solar-heating-and-cooling-market-industry-and-policy
- IRENA offers various trainings regarding solar water heating, e.g. Solar Water Heating Project Feasibility Analysis Course
- How to set up a test laboratory for Solar Water Heater (2015) by Research and Testing Centre for Thermal Solar Systems (TZS) Stephan Fischer: Rica/8-Setup test lab SWH -Stephan Fischer.pdf http://www.irena.org/EventDocs/Costa Rica/8-Setup test lab SWH -Stephan Fischer.pdf
- IRENA held a Forum on Quality Assurance Schemes for Solar Water Heating in Latin America and the Caribbean 29-30 June 2015 in San Jose, Costa Rica. http://www.irena.org/menu/index.aspx?CatID=79&PriMenuID=30&SubcatID=623&mnu=Subcat
- Introduction to solar thermal technology: https://energypedia.info/images/9/95/Solar_Thermal_Energy_Basis_Mr_Kofler_ITW.pdf
- Solar Heat for Industrial Processes in Tunisia: An Economic Assessment with Policy Recommendations (2014) by Filip Schaffitzel https://energypedia.info/images/e/e7/Solar_Heat_for_Industrial_Process_in_Tunisia._An_Economic_Assessment_with_Policy_Recommendations.pdf
- FSEC Public Information Office. ‘Solar Water Heater Troubleshooting Checklist’. Florida Solar Energy Center. Accessed 9 March 2017. http://www.fsec.ucf.edu/en/publications/pdf/FSEC-FS-32-86.pdf
- John Harrison & Tom Tiedeman. ‘Thermosyphon Systems - Passive Solar Water Heating Systems’, 1997. http://www.flasolar.com/thermosyphon_systems.htm
References
- ↑ Ashok Gadgil et al., ‘Domestic Solar Water Heater for Developing Countries’, Http://Energy. Lbl. Gov/Staff/Gadgil/Docs/2007/Solar-Water-Heater-Rpt. Pdf. Accessed on 6, no. 04 (2007): 2013.
- ↑ David Elizinga et al., ‘ADVANTAGE ENERGY Emerging Economies, Developing Countries and the Private-Public Sector Interface’ (Internationale Energy Agency, 2011), http://www.iea.org/publications/freepublications/publication/advantage_energy.pdf.
- ↑ Amy Punter, ‘Solar Thermal Energy Application Heating,cooling, Crop Drying - Practical Answers’, 2007, http://answers.practicalaction.org/our-resources/item/solar-thermal-energy.
- ↑ 4.0 4.1 GTZ (2007): Eastern Africa Resource Base: GTZ Online Regional Energy Resource Base: Regional and Country Specific Energy Resource Database: I - Energy Technology
- ↑ 5.0 5.1 https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/File:DirectSolarSystems.jpg
- ↑ 6.0 6.1 UNEP (2015): Solar Water Heating, a Strategic Planning Guide for Cities in Developing Countries http://www.estif.org/fileadmin/estif/content/publications/downloads/UNEP_2015/unep_report_cities_lr.pdf Cite error: Invalid
<ref>tag; name "UNEP (2015): Solar Water Heating, a Strategic Planning Guide for Cities in Developing Countries http://www.estif.org/fileadmin/estif/content/publications/downloads/UNEP_2015/unep_report_cities_lr.pdf" defined multiple times with different content - ↑ Ray Holland, ‘Solar Water Heaters: Hot Water for Washing and Heating - Practical Answers’, 1988, http://answers.practicalaction.org/our-resources/item/solar-water-heating.
- ↑ Deutsche Energie-Agentur GmbH (dena), ‘Solar Thermal Energy Technologies and Applications’, 17 December 2014, http://www.renewables-made-in-germany.com/en/renewables-made-in-germany/technologies/solar-thermal-energy/solar-thermal-energy/technologies-and-applications.html.
- ↑ 9.0 9.1 Jean Cariou and Peter Meisen, ‘Solar Water Heater’, Global Energy Network Institute, 2010, http://www.solarthermalworld.org/sites/gstec/files/story/2015-06-21/solar-water-heater.pdf.
- ↑ https://energy.gov/energysaver/estimating-cost-and-energy-efficiency-solar-water-heater
- ↑ International Renewable Energy Agency (IRENA) and Energy Technology Systems Analysis Programme (ETSAP, ‘Solar Heating and Cooling for Residential Applications | Technology Brief’, 2015, http://www.irena.org/DocumentDownloads/Publications/IRENA_ETSAP_Tech_Brief_R12_Solar_Thermal_Residential_2015.pdf.
- ↑ 12.0 12.1 12.2 12.3 International Renewable Energy Agency (IRENA) and Energy Technology Systems Analysis Programme (ETSAP, ‘Solar Heating and Cooling for Residential Applications | Technology Brief’.
- ↑ GTZ (2007): Eastern Africa Resource Base: GTZ Online Regional Energy Resource Base: Regional and Country Specific Energy Resource Database: I - Energy Technology
- ↑ US Department of Energy, ‘A Consumer’s Guide HeatYourWaterwiththeSun’, 2003, http://solarteknologies.com/pdfs/brochures/water_heat_guide.pdf.
- ↑ Ashok Gadgil et al., ‘Solar Water Heater Project’, 2009, http://www.solarthermalworld.org/sites/gstec/files/story/2015-06-21/swh-rpt-2009.pdf.
- ↑ Source?
- ↑ http://endev-bolivia.org/images/stories/proyecto_endev/infraestructura/Descargas/Difusion/lecsaprendidas.pdf
- ↑ 21.0 21.1 Anna Brüderle, Johanna Hartmann, and Katja Diembeck, ‘Productive Use of Thermal Energy An Overview of Technology Options and Approaches for Promotion’ (Deutsche Gesellschaft für Internationale Zusammenarbeit (GIZ) GmbH - Programme - Poverty-oriented Basic Energy Services (HERA) and European Union Energy Initiative Partnership Dialogue Facility (EUEI PD, 2014), https://energypedia.info/images/2/24/Productive_Use_of_Thermal_Energy_Overview.pdf.
- ↑ http://www.solarthermalworld.org/content/tunisia-government-extends-prosol-support-scheme
- ↑ https://climatepolicyinitiative.org/publication/san-giorgio-group-case-study-prosol/
- ↑ Deutsche Energie-Agentur GmbH (dena), ‘Renewable Energy Solutions for Off-Grid Applications. Providing Electric Power and Heat for Regions without Grid Power or Connected to a Weak Grid’, 2013, http://www.renewables-made-in-germany.com/fileadmin/user_upload/Auslandsmarketing/Offgrid_2013_131020.pdf.
- ↑ Trudy Forsyth et al., ‘Quality Infrastructure for Renewable Energy Technologies: Solar Water Heaters’ (International Renewable Energy Agency (IRENA), 2015), http://www.irena.org/DocumentDownloads/Publications/IRENA_QI_3_SWH_2015.pdf.
- ↑ 26.0 26.1 26.2 Alessandro Clerici and World Energy Council, World Energy Resources. 2013 Survey (London: World Energy Council, 2013).
- ↑ 27.0 27.1 27.2 Janet L. Sawin, et al., ‘RENEWABLES 2016. GLOBAL STATUS REPORT. Key Findings 2016’ (REN21, 2016), http://www.ren21.net/wp-content/uploads/2016/06/GSR_2016_KeyFindings1.pdf.
- ↑ SolaRwanda program, ‘Introduction to Solar Water Heaters. Frequently Asked Questions on Solar Water Heaters’.
- ↑ Global Solar Water Heating Market Transformation and Strengthening Initiative (GSWH Project, ‘Solar Heating and Cooling Application Factsheet: Domestic Water Heaters for Social Amenities’.