Difference between revisions of "Photovoltaic (PV) Pumping"
***** (***** | *****) m |
***** (***** | *****) m |
||
| Line 49: | Line 49: | ||
<br/> | <br/> | ||
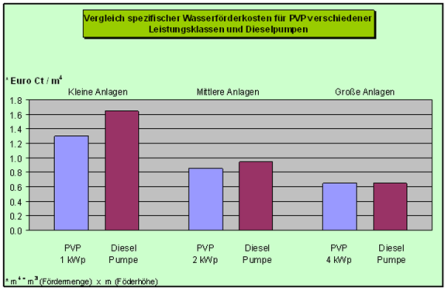
| − | [[File:Pv pumping costs.png|frame|center|180px|Pv pumping costs.png]] | + | [[File:Pv pumping costs.png|frame|center|180px|Pv pumping costs.png]] |
= Irrigation<br/> = | = Irrigation<br/> = | ||
| Line 65: | Line 65: | ||
== Case Study:India == | == Case Study:India == | ||
| − | For information about use of pumping system for irrigation in India, see [[ | + | For information about use of pumping system for irrigation in India, see [[Photovoltaic (PV) Pumping Systems for Irrigation|Photovoltaic (PV) Pumping Systems for Irrigation]] |
| + | |||
| + | == Case Study:Jordan == | ||
| + | |||
| + | For information about large scale solar pumping in agriculture in Jordan, see [[Prospects_of_Large_Scale_Solar_Water_Pumping_Applications_for_Agriculture_with_a_Case_Study_from_Jordan|Prospects of Large Scale Solar Water Pumping Applications for Agriculture with a Case Study from Jordan]] | ||
= Project Experiences<br/> = | = Project Experiences<br/> = | ||
| Line 78: | Line 82: | ||
*[[Portal:Solar|Solar portal on energypedia]]<br/> | *[[Portal:Solar|Solar portal on energypedia]]<br/> | ||
| − | *[[ | + | *[[Design of Photovoltaic (PV) Pumping|Design of Photovoltaic (PV) Pumping]] |
*GIZ INTERNAL: [https://dms.gtz.de/livelink-ger/livelink.exe?func=ll&objId=57642651&objAction=browse DMS folder]containing additional documents on PV pumping (documents also available upon request from [mailto:hera@gtz.de GTZ-HERA]) | *GIZ INTERNAL: [https://dms.gtz.de/livelink-ger/livelink.exe?func=ll&objId=57642651&objAction=browse DMS folder]containing additional documents on PV pumping (documents also available upon request from [mailto:hera@gtz.de GTZ-HERA]) | ||
*[http://net.grundfos.com/doc/webnet/renewables/solar.html Product overview] and [http://net.grundfos.com/doc/webnet/renewables/cases.html cases] of market leader Grundfos | *[http://net.grundfos.com/doc/webnet/renewables/solar.html Product overview] and [http://net.grundfos.com/doc/webnet/renewables/cases.html cases] of market leader Grundfos | ||
*[[Decentralized Drinking Water Supply|Drinking water supply]] | *[[Decentralized Drinking Water Supply|Drinking water supply]] | ||
*[http://agriwaterpedia.info/wiki/Solar_Powered_Water_Pumps Solar Powered Water Pumps]: overview of the strengths, weaknesses, opportunities and threats of photovoltaic pumps (PVP) | *[http://agriwaterpedia.info/wiki/Solar_Powered_Water_Pumps Solar Powered Water Pumps]: overview of the strengths, weaknesses, opportunities and threats of photovoltaic pumps (PVP) | ||
| + | *[[:File:Solarpumpen_zur_Bewässerung-Erfahrungen,_Status_und_Perspektiven_-.pdf|Solarpumpen zur Bewässerung-Erfahrungen, Status und Perspektiven -.pdf]]<br/> | ||
<br/> | <br/> | ||
| Line 90: | Line 95: | ||
<references /> | <references /> | ||
| + | [[Category:Pumping]] | ||
| + | [[Category:Jordan]] | ||
| + | [[Category:India]] | ||
| + | [[Category:Solar]] | ||
[[Category:Water_Supply]] | [[Category:Water_Supply]] | ||
| − | |||
| − | |||
Revision as of 09:38, 4 August 2014
Introduction
Drinking Water Supply
PVP -Power
|
Head [m]
|
Flow Rate [m³]
|
People Supplied (Consuming 25 l/c*d)
|
1 kWp (equals about 500 m4/day)
|
10 30 50
|
50 15 10
|
2000 600 400
|
2 kWp (equals about 1000 m4/day)
|
10 30 50
|
100 35 20
|
4000 1400 800
|
4 kWp (equals about 2000 m4/day)
|
10 30 50
|
200 65 40
|
8000 2600 1600
|
Average Investment [Euro]
|
1 kWp
|
2 kWp
|
4 kWp
|
Pumping System (PV-Generator, Inverter, Pump)
|
8000
|
15000
|
25000
|
Ready-to-operate PV Pumping System (Pumping system, logistics, set-up, reservoir, construction, water distribution)
|
16000
|
25000
|
41000
|
Irrigation
- In order to reduce the energy requirements of PVP irrigation systems water-conserving and energy-saving micro-irrigation techniques have to be applied.
- The plot size for PVP irrigation should be below 4 hectares.
- High rates of system utilisation are necessary to achieve economic viability of PVP irrigation systems.
- Therefore PVP systems are limited to irrigate permanent crops and continuous crop rotation in arid climates.
- High value-added cash crops like fruits, vegetables and spices should be given preference to recoup the high initial investment.
- Low-interest loans should be available for the same reason.
- PVP irrigation systems require a careful planning of the crop schedule and are more demanding of user skills.
Case Study:India
For information about use of pumping system for irrigation in India, see Photovoltaic (PV) Pumping Systems for Irrigation
Case Study:Jordan
For information about large scale solar pumping in agriculture in Jordan, see Prospects of Large Scale Solar Water Pumping Applications for Agriculture with a Case Study from Jordan
Project Experiences
Gesellschaft für Internationale Zusammenarbeit (GIZ) has experience of PVP irrigation in projects in Chile (smallholder farmers), Ethiopia (tree nursery Forestry Dep.) and Bangladesh (irrigation of paddy fields).
Experience in Bangladesh has shown that PV panels can have significant spatial requirements depending on the energy needed. This leads to disadvantages for farmers. KfW(German Development Bank) has supported the installation and dissemination of PVP pumps for irrigation in several countries in sub-Saharan Africa (Eritrea, Guinea, Mali, Namibia, Burkina Faso). At experimental level there are already technical solutions available for the application of PVP in stand-alone systems to irrigate an area of 30-40 hectares by using variable frequency drives (VFD) for any AC-motor.
Further Information
- Solar portal on energypedia
- Design of Photovoltaic (PV) Pumping
- GIZ INTERNAL: DMS foldercontaining additional documents on PV pumping (documents also available upon request from GTZ-HERA)
- Product overview and cases of market leader Grundfos
- Drinking water supply
- Solar Powered Water Pumps: overview of the strengths, weaknesses, opportunities and threats of photovoltaic pumps (PVP)
- Solarpumpen zur Bewässerung-Erfahrungen, Status und Perspektiven -.pdf