Difference between revisions of "Fuel Prices Thailand"
***** (***** | *****) m |
***** (***** | *****) |
||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
{{Fuel Price Factsheet | {{Fuel Price Factsheet | ||
|Fuel Price Country=Thailand | |Fuel Price Country=Thailand | ||
| + | |Fuel Pricing Policies=The downstream market in Thailand is liberal. The Energy Policy & Planning Office (EPPO) publishes very comprehensive information on fuel prices, monitored retail prices, monitored wholesale prices, refinery prices and levies/taxation. For all of these data, also historical data is available on their website (http://www.eppo.go.th/info/8prices_stat.htm). | ||
| + | |||
| + | Thailand uses an oil fund to flatten out volatile world market prices. Fuels are either subsidized or an oil fund levy is imposed in times of low oil costs. In December 2010, the government decided to begin subsidizing Diesel using the oil fund (see 2). Gasoline remained un-subsidized, and an oil fund levy of 7.5 Baht is imposed for gasoline. Hence, gasoline users cross-subsidize Diesel users. | ||
| + | |||
| + | As of April 2011, the subsidies for Diesel reached 4.5 Baht per litre (almost three times more than in January, shown in 2.; →see App A1). The balance of the oil fund rapidly approached zero. As a reaction, the government reduced Excise Tax on Diesel to almost zero (which also can be seen as a subsidy, when compared to other fuels). The whole issue of subsidizing Diesel is critically discussed by local experts, who recommend an end or an reduction of the subsidies, as they could produce a high burden to the national budget as soon as the oil fund balance reaches zero (→App. A3). | ||
| + | |||
| + | "The Oil Fund is used to cross-subsidize fuel prices, and in addition the ex-refinery price of LPG is heavily subsidized, resulting in a large subsidy burden. Government stopped posting monthly information on the balance of the Oil Fund on the Web site of Energy Policy and Planning Office (EPPO) of Ministry of Energy in 2011 in the months leading up to a closely contested general election in July, and has not resumed since. Government subsidizes the prices of LPG and biofuels, and in recent years diesel. In 2011, the issue at hand was how long government could prevent the diesel price from rising above 30 baht (US$1/liter). The Oil Fund had a deficit of 22 billion baht (US$0.7 billion) in Jun 2012. Government’s plan to float the price of LPG for industries in 2008 faced strong opposition and was delayed until Jul 2011, when the price began to be raised by 3 baht/kg every three months until it reached 30.13 baht/kg; price increases above 30.13 baht/kg would require the approval of the National Energy Policy Council, chaired by the prime minister. Many companies switched to 48-kg cylinders, normally reserved for household use. The price of automotive LPG began to be raised in 2012. The LPG subsidy is borne by government and the CNG subsidy by PTT (formerly known as Petroleum Authority of Thailand), and hence government has used the Oil Fund to finance conversion of taxis from LPG to CNG. The Oil Fund received authorization to borrow 10 billion baht (US$0.32 billion) in Oct 2011, and another 20 billion baht (US$0.65 billion) in Mar 2012. In Apr 2011, the cabinet approved a cut in the excise tax and VAT for diesel from 5.83 baht (US$0.19) per liter to 0.005 baht effective from on Apr 21 until Sep 30 to keep diesel price at or below 30 baht a liter, a move widely criticized for being political even by the Federation of Thai Industries. In Jul 2011, the Excise Department said the decision had led to higher diesel consumption and government had lost 9 billion baht (US$300 million) a month. Government has fixed the ex-refinery price of LPG at US$333 per tonne for more than two decades under a program intended originally to help relieve the burden of households and food vendors. Government in Aug 2011 suspended contributions of 91 and 95 RON gasoline and diesel to the Oil Fund. Officials were sent to 18,000 filling stations nationwide to check the amount of stocks before the new prices became effective; government had set aside about 3 billion baht (US$100 million) to compensate retailers for the inventory. PTT is eventually reimbursed for LPG subsidy, but with a long delay." (Source: Kojima, Masami. (2013, forthcoming). “Petroleum product pricing and complementary policies:Experience of 65 developing countries since 2009.” Washington DC: World Bank.) | ||
|Fuel Currency=THB | |Fuel Currency=THB | ||
|Fuel Price Exchange Rate=29.83 | |Fuel Price Exchange Rate=29.83 | ||
| Line 12: | Line 19: | ||
Source: Own calculations based on http://www.eppo.go.th/info/8prices_stat.htm and →App. A1 | Source: Own calculations based on http://www.eppo.go.th/info/8prices_stat.htm and →App. A1 | ||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
|Fuel Matrix Pricing Mechanism=3 | |Fuel Matrix Pricing Mechanism=3 | ||
|Fuel Matrix Price Level=2.5 | |Fuel Matrix Price Level=2.5 | ||
Revision as of 15:05, 13 February 2013
Part of: GIZ International Fuel Price database
Also see: Thailand Energy Situation
Fuel Pricing Policies
| Local Currency: | THB |
| Exchange Rate: | 29.83
|
| Last Update: |
The downstream market in Thailand is liberal. The Energy Policy & Planning Office (EPPO) publishes very comprehensive information on fuel prices, monitored retail prices, monitored wholesale prices, refinery prices and levies/taxation. For all of these data, also historical data is available on their website (http://www.eppo.go.th/info/8prices_stat.htm).
Thailand uses an oil fund to flatten out volatile world market prices. Fuels are either subsidized or an oil fund levy is imposed in times of low oil costs. In December 2010, the government decided to begin subsidizing Diesel using the oil fund (see 2). Gasoline remained un-subsidized, and an oil fund levy of 7.5 Baht is imposed for gasoline. Hence, gasoline users cross-subsidize Diesel users.
As of April 2011, the subsidies for Diesel reached 4.5 Baht per litre (almost three times more than in January, shown in 2.; →see App A1). The balance of the oil fund rapidly approached zero. As a reaction, the government reduced Excise Tax on Diesel to almost zero (which also can be seen as a subsidy, when compared to other fuels). The whole issue of subsidizing Diesel is critically discussed by local experts, who recommend an end or an reduction of the subsidies, as they could produce a high burden to the national budget as soon as the oil fund balance reaches zero (→App. A3).
"The Oil Fund is used to cross-subsidize fuel prices, and in addition the ex-refinery price of LPG is heavily subsidized, resulting in a large subsidy burden. Government stopped posting monthly information on the balance of the Oil Fund on the Web site of Energy Policy and Planning Office (EPPO) of Ministry of Energy in 2011 in the months leading up to a closely contested general election in July, and has not resumed since. Government subsidizes the prices of LPG and biofuels, and in recent years diesel. In 2011, the issue at hand was how long government could prevent the diesel price from rising above 30 baht (US$1/liter). The Oil Fund had a deficit of 22 billion baht (US$0.7 billion) in Jun 2012. Government’s plan to float the price of LPG for industries in 2008 faced strong opposition and was delayed until Jul 2011, when the price began to be raised by 3 baht/kg every three months until it reached 30.13 baht/kg; price increases above 30.13 baht/kg would require the approval of the National Energy Policy Council, chaired by the prime minister. Many companies switched to 48-kg cylinders, normally reserved for household use. The price of automotive LPG began to be raised in 2012. The LPG subsidy is borne by government and the CNG subsidy by PTT (formerly known as Petroleum Authority of Thailand), and hence government has used the Oil Fund to finance conversion of taxis from LPG to CNG. The Oil Fund received authorization to borrow 10 billion baht (US$0.32 billion) in Oct 2011, and another 20 billion baht (US$0.65 billion) in Mar 2012. In Apr 2011, the cabinet approved a cut in the excise tax and VAT for diesel from 5.83 baht (US$0.19) per liter to 0.005 baht effective from on Apr 21 until Sep 30 to keep diesel price at or below 30 baht a liter, a move widely criticized for being political even by the Federation of Thai Industries. In Jul 2011, the Excise Department said the decision had led to higher diesel consumption and government had lost 9 billion baht (US$300 million) a month. Government has fixed the ex-refinery price of LPG at US$333 per tonne for more than two decades under a program intended originally to help relieve the burden of households and food vendors. Government in Aug 2011 suspended contributions of 91 and 95 RON gasoline and diesel to the Oil Fund. Officials were sent to 18,000 filling stations nationwide to check the amount of stocks before the new prices became effective; government had set aside about 3 billion baht (US$100 million) to compensate retailers for the inventory. PTT is eventually reimbursed for LPG subsidy, but with a long delay." (Source: Kojima, Masami. (2013, forthcoming). “Petroleum product pricing and complementary policies:Experience of 65 developing countries since 2009.” Washington DC: World Bank.)
Fuel Prices and Trends
| Gasoline 95 Octane | Diesel | |
|---|---|---|
| in USD* |
|
|
| in Local Currency |
|
|
* benchmark lines: green=US price; grey=price in Spain; red=price of Crude Oil
Fuel Price Composition
Price composition for one litre of High Speed Diesel as of 2012/01/01.
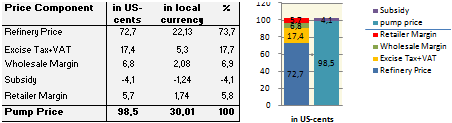
Source: Own calculations based on http://www.eppo.go.th/info/8prices_stat.htm and →App. A1
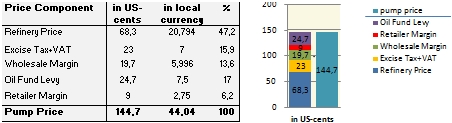
Price composition for one litre of 95-octane gasoline as of January 2011
Source: Own calculations based on http://www.eppo.go.th/info/8prices_stat.htm and →App. A1
At a Glance
| Regulation-Price-Matrix |
| ||||
 |

|

|

| ||
An easy-to-understand price breakdown might be added to the informations given at http://www.eppo.go.th. Information on fuel taxes missing as of May 21st, 2011.
Sources to the Public
| Type of Information | Web-Link / Source |
|---|---|
| Price Composition | http://www.eppo.go.th/info/8prices_stat.htm (Implicitly available from given data) |
| Pump prices and margins | http://www.eppo.go.th/info/8prices_stat.htm |
| Wholesale Prices | http://www.eppo.go.th/info/8prices_stat.htm |
Contact
Please find more information on GIZ International Fuel Price Database and http://www.giz.de/fuelprices
"High Speed Diesel" contains an extrinsic dash or other characters that are invalid for a date interpretation.















