Difference between revisions of "Barriers and Risks to Renewable Energy Financing"
***** (***** | *****) m |
***** (***** | *****) m (→Overview) |
||
| Line 3: | Line 3: | ||
[[Portal:Financing and Funding|► Back to Financing & Funding Portal]]<br/> | [[Portal:Financing and Funding|► Back to Financing & Funding Portal]]<br/> | ||
| + | |||
= Overview = | = Overview = | ||
| Line 12: | Line 13: | ||
*On the'''supply side '''of RE finance there are several shortcomings in the financial sector especially in developing countries where there might be no supply at all. | *On the'''supply side '''of RE finance there are several shortcomings in the financial sector especially in developing countries where there might be no supply at all. | ||
*'''Framework conditions''' for projects within the energy sector can include substantial burden and barriers for RE finance<ref name="Lindlein, P. & Mostert, W., 2005. Financing Renewable Energies - Instruments, Strategies, Practice Approaches, KfW.">Lindlein, P. & Mostert, W., 2005. Financing Renewable Energies - Instruments, Strategies, Practice Approaches, KfW.</ref>.<span style="line-height: 1.5em; font-size: 0.85em;"></span> | *'''Framework conditions''' for projects within the energy sector can include substantial burden and barriers for RE finance<ref name="Lindlein, P. & Mostert, W., 2005. Financing Renewable Energies - Instruments, Strategies, Practice Approaches, KfW.">Lindlein, P. & Mostert, W., 2005. Financing Renewable Energies - Instruments, Strategies, Practice Approaches, KfW.</ref>.<span style="line-height: 1.5em; font-size: 0.85em;"></span> | ||
| + | |||
| + | <br/> | ||
| + | |||
| + | [[File:Barriers to RE1.PNG|thumb|center|300px|Barriers for RE in the Steps Towards Financial Closure. Source: Lindlein, P. & Mostert, W., 2005. Financing Renewable Energies - Instruments, Strategies, Practice Approaches, KfW.]] | ||
<br/> | <br/> | ||
| Line 447: | Line 452: | ||
<br/> | <br/> | ||
| + | |||
= Financing Barriers = | = Financing Barriers = | ||
Revision as of 11:00, 16 August 2013
► Back to Financing & Funding Portal
Overview
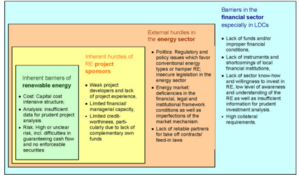
There are a number of key risks and barriers that can threaten investment in renewable energy (RE) projects and thus prevent the uptake of desirable technologies.
Lindlein & Mostert (2005)[1] have suggested that it is appropriate to group these barriers by the market categories supply, demand and framework conditions. From this view the most pervasive barriers to financing renewable energy from demand to supply are categorised as:
- Demand side barriers due to the characteristics of RE projects and internal problems of RE project sponsors.
- On thesupply side of RE finance there are several shortcomings in the financial sector especially in developing countries where there might be no supply at all.
- Framework conditions for projects within the energy sector can include substantial burden and barriers for RE finance[1].
At a broad macro-economic level, barriers to RE investment can be categorised as follows[2]:
- Cognitive Barriers. Theses relate to the low level of awareness, understanding and attention afforded to RE financing and risk management instruments particularly in low income countries.
- Political Barriers. These are associated with regulatory and policy issues and governmental leadership.
- Analytical Barriers: these relate to the quality and availability of information necessary for prudent underwriting, developing quantitative analytical methodologies for risk management instruments and creating useful pricing models for environmental markets such as carbon emissions permits.
- Market Barriers: these are associated with lack of financial, legal and institutional frameworks to support the uptake of RE projects in different jurisdictions.
Technological Differences
Different RE technologies have different degrees of exposure to the various barriers and risks due to their specifics and maturity.
The table below highlights some of the key risk issues affecting different RE technologies. Technology and operational risks are the principal deterrents to attracting appropriate commercial insurance cover[2].
Key Risks & Barriers Associated with RE Projects | ||
RET Type |
Key Risk Issues |
Risk Management Considerations |
|
Geothermal
|
|
|
|
Large PV
|
|
|
|
Solar thermal
|
|
|
|
Small hydropower
|
|
|
|
Wind power
|
|
|
|
Biomass power
|
|
|
|
Biogas power
|
|
|
|
Tidal/wave power |
|
|
|
Notes: * The probability of success in achieving (economically acceptable) minimum levels in thermal water production (minimum flow rates) and reservoir temperatures. **Stimulation technology attempts to improve natural productivity or to recover lost productivity from geothermal wells through various techniques including chemical and explosive stimulation. | ||
Source:[2]
Generally all large RET projects will require access to long term funding on a project finance basis, but their exposure to their barriers and risks will differ. Thus the need to obtain pre-investment financing and other project development processes will be more significant for hydro projects and less so for other technologies that do not have the same impacts on land use and on downstream communities[3].
Thus project sizes and transaction cost barriers are generally lower for wind and geothermal projects that can be developed on a greater scale than other technologies.
Geothermal and small hydro can be competitive with conventional technologies, and wind energy is also approaching competitiveness in some countries. However, solar technologies remain a long way from achieving cost competitiveness; therefore its affordability remains a key risk[3].
Resource uncertainties are also a problem for all technologies, though in differing ways:
- Geothermal projects have the greatest risk at the time of resource appraisal, when the expensive drilling of exploratory wells is needed.
- Biomass projects have a significant problem with the continuing availability of affordable and adequate resources.
- Technologies dependent on carbon financing are likely to be more vulnerable to the resource uncertainty problem.
Off-Grid Projects:
- These projects face different problems from those on non-grid RET projects. Off-grid projects are generally reliant on sales of individual household or small scale systems to rural communities. Technical challenges may be limited but affordability and financeability are key.
- The very small scale of such projects, down to the individual household level, means transaction costs can become an overwhelming barrier.
- The lack of long term project financing is less of a barrier to such projects, due to their very small size, they typically rely on corporate finance or on customer purchases[3].
The figure below shows the significance of barriers and risks to different technologies, providing an indication of which barriers and risk are likely to pose the greatest challenges to developing RETs.
| Technologies & Barriers and Risks | |||||||||||
|
|
Financing Barriers |
Project Risks | |||||||||
|
|
Lack of Long-term Financing |
Lack of Project Financing |
High & Uncertain Project Development Costs |
Lack of Equity Finance |
Small Scale of Projects |
High Financial Cost |
High Exposure to Regulatory Risk |
Uncertainty Over Carbon Financing |
High Costs of Resource Assessments |
Uncertainty over Resource Adequacy | |
|
On-Grid |
| ||||||||||
|
Wind |
Hi |
Med |
Lo |
Lo |
Lo |
Med |
Med |
Med |
Lo |
Med | |
|
Solar |
Hi |
Med |
Lo |
Med |
Med |
Hi |
Med |
Med |
Lo |
Med | |
|
Small Hydro |
Hi |
Med |
Med |
Med |
Lo |
Lo |
Med |
Lo |
Med |
Hi | |
|
Biomass |
Hi |
Med |
Lo |
Lo |
Med |
Med |
Med |
Med |
Lo |
Hi | |
|
Geothermal |
Med |
Med |
Hi |
Med |
Lo |
Lo |
Med |
Lo |
Hi |
Med | |
|
Off-grid |
| ||||||||||
|
Solar/Micro-hydro |
Med |
Lo |
Med |
Hi |
Hi |
Med |
Lo |
Lo |
Lo |
Med | |
Source: Adapted from The World Bank, 2013. Financing Renewable Energy - Options for Developing Financing Instruments Using Public Funds[3].
Note – Lo = Small/no impact (mitigation of risks is desirable.) Med = Moderate impact (mitigation of risks is less likely to be required.) Hi = Significant impact (mitigation of risks is generally necessary if the project is to proceed.
Financing Barriers
Risks of Renewable Energy Projects
Further Information
References
- ↑ 1.0 1.1 Lindlein, P. & Mostert, W., 2005. Financing Renewable Energies - Instruments, Strategies, Practice Approaches, KfW.
- ↑ 2.0 2.1 2.2 United Nations Environment Programme (UNEP), 2004. Financial Risk Management Instruments for Renewable Energy Projects - Summary Document, UNEP, Division of Technology, Industry and Economics.
- ↑ 3.0 3.1 3.2 3.3 The World Bank, 2013. Financing Renewable Energy - Options for Developing Financing Instruments Using Public Funds.