Knowledge fuels change - Support energypedia!
For over 10 years, energypedia has been connecting energy experts around the world — helping them share knowledge, learn from each other, and accelerate the global energy transition.
Today, we ask for your support to keep this platform free and accessible to all.
Even a small contribution makes a big difference! If just 10–20% of our 60,000+ monthly visitors donated the equivalent of a cup of coffee — €5 — Energypedia would be fully funded for a whole year.
Is the knowledge you’ve gained through Energypedia this year worth €5 or more?
Your donation keeps the platform running, helps us create new knowledge products, and contributes directly to achieving SDG 7.
Thank you for your support, your donation, big or small, truly matters!
Difference between revisions of "Fuel Prices Vietnam"
***** (***** | *****) m (Protected "Fuel Prices Vietnam" ([edit=sysop] (indefinite) [move=sysop] (indefinite)) [cascading]) |
***** (***** | *****) |
||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
{{Fuel Price Factsheet | {{Fuel Price Factsheet | ||
|Fuel Price Country=Vietnam | |Fuel Price Country=Vietnam | ||
| + | |Fuel Pricing Policies=Petrolimex is the national petroleum corporation in Vietnam. Fuel prices follow a formula, based on import prices (Singapore spot market prices) and several margins, taxes and levies. The price is calculated and published daily by Petrolimex. In the daily newsletter publication, not only pump prices, but also the complete price breakdown is being published. | ||
| + | |||
| + | Vietnam has a stabilization fund for oil products, which is used to lower pump prices at times of import price peaks. As of March 2011, the value is positive, i.e. every sold litre of gasoline or diesel brings 300 Dong into the fund. | ||
| + | |||
| + | Historical timelines/statistics of fuelprices could not be found on the Petrolimes website (http://www.petrolimex.com.vn/). | ||
| + | |||
| + | "Vietnam has a price stabilization fund and every liter sold contributes to it, with the contribution varying from time to time. Until recently, fuel prices were set by government with irregular adjustments. Since mid-2012, price adjustments have been more market-based, with wholesalers allowed to adjust prices (although still subject to final government approval). Where price adjustments exceeding 7% are necessary, government is to consider other options to stabilize prices, such as reducing import tariffs and drawing down on the stabilization fund. Government was going to start deregulating prices in May 2007 but stopped because of price volatility. Government abolished subsidies to importers, but they were not allowed to raise retail prices without approval from the trade and finance ministries. With increases in retail prices failing to stay in line with rising international prices, importers suffered from negative margins. Import tariffs on gasoline and jet fuel were abolished in Feb 2012 and on diesel and kerosene in Mar 2012. Government has historically adjusted import tariffs frequently to smooth retail prices. The stabilization fund was D703 billion (US$33 million) in the deficit in early 2011. In Apr 2012, Ministry of Trade abd Industry said outflows from the fund exceeded inflows by more than D2.3 trillion (US$110 million), and yet still leaving companies with losses of D5 trillion (US$239 million)." (Source: Kojima, Masami. (2013, forthcoming). “Petroleum product pricing and complementary policies:Experience of 65 developing countries since 2009.” Washington DC: World Bank.) | ||
|Fuel Currency=VND | |Fuel Currency=VND | ||
|Fuel Price Exchange Rate=19271 | |Fuel Price Exchange Rate=19271 | ||
|Fuel Price Exchange Rate Date=2010/11/17 | |Fuel Price Exchange Rate Date=2010/11/17 | ||
| − | |||
|Fuel Price Composition=GIZ_IFP2012_Vietnam1.png | |Fuel Price Composition=GIZ_IFP2012_Vietnam1.png | ||
|Fuel Price Composition Fuel Type=Gasoline 92 Octane | |Fuel Price Composition Fuel Type=Gasoline 92 Octane | ||
| Line 18: | Line 24: | ||
Source: http://www.petrolimex.com.vn/ | Source: http://www.petrolimex.com.vn/ | ||
| − | |Fuel Pricing | + | |Fuel Matrix Pricing Mechanism=2 |
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
|Fuel Matrix Price Level=2 | |Fuel Matrix Price Level=2 | ||
| − | |||
|Fuel Matrix Annotation=Historical fuel price data missing. | |Fuel Matrix Annotation=Historical fuel price data missing. | ||
|Fuel Transparency Price Composition=3 | |Fuel Transparency Price Composition=3 | ||
Revision as of 19:40, 8 February 2013
Part of: GIZ International Fuel Price database
Also see: Vietnam Energy Situation
Fuel Pricing Policies
| Local Currency: | VND |
| Exchange Rate: | 19271
|
| Last Update: |
Petrolimex is the national petroleum corporation in Vietnam. Fuel prices follow a formula, based on import prices (Singapore spot market prices) and several margins, taxes and levies. The price is calculated and published daily by Petrolimex. In the daily newsletter publication, not only pump prices, but also the complete price breakdown is being published.
Vietnam has a stabilization fund for oil products, which is used to lower pump prices at times of import price peaks. As of March 2011, the value is positive, i.e. every sold litre of gasoline or diesel brings 300 Dong into the fund.
Historical timelines/statistics of fuelprices could not be found on the Petrolimes website (http://www.petrolimex.com.vn/).
"Vietnam has a price stabilization fund and every liter sold contributes to it, with the contribution varying from time to time. Until recently, fuel prices were set by government with irregular adjustments. Since mid-2012, price adjustments have been more market-based, with wholesalers allowed to adjust prices (although still subject to final government approval). Where price adjustments exceeding 7% are necessary, government is to consider other options to stabilize prices, such as reducing import tariffs and drawing down on the stabilization fund. Government was going to start deregulating prices in May 2007 but stopped because of price volatility. Government abolished subsidies to importers, but they were not allowed to raise retail prices without approval from the trade and finance ministries. With increases in retail prices failing to stay in line with rising international prices, importers suffered from negative margins. Import tariffs on gasoline and jet fuel were abolished in Feb 2012 and on diesel and kerosene in Mar 2012. Government has historically adjusted import tariffs frequently to smooth retail prices. The stabilization fund was D703 billion (US$33 million) in the deficit in early 2011. In Apr 2012, Ministry of Trade abd Industry said outflows from the fund exceeded inflows by more than D2.3 trillion (US$110 million), and yet still leaving companies with losses of D5 trillion (US$239 million)." (Source: Kojima, Masami. (2013, forthcoming). “Petroleum product pricing and complementary policies:Experience of 65 developing countries since 2009.” Washington DC: World Bank.)
Fuel Prices and Trends
| Gasoline 95 Octane | Diesel | |
|---|---|---|
| in USD* |
|
|
| in Local Currency |
|
|
* benchmark lines: green=US price; grey=price in Spain; red=price of Crude Oil
Fuel Price Composition
Price composition for one litre of Gasoline 92 Octane as of 2011/03/29.
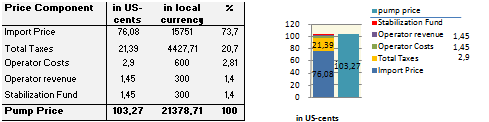
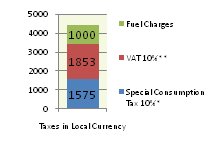
(*The Special Consumption Tax is 10% of import price (incl. import tax, which is 0% as of March 2011))
(**VAT is 10% of pump price minus Fuel Charge of 1000 Dong.)
Import Price is the 30-day-average Singapore spot market price.
As of March 2011, there is no „Fuel Charge“ on diesel.
Source: http://www.petrolimex.com.vn/
At a Glance
| Regulation-Price-Matrix |
| ||||
 |

|

|

| ||
Historical fuel price data missing.
Sources to the Public
| Type of Information | Web-Link / Source |
|---|---|
| Other Information | http://www.petrolimex.com.vn/ |
| Price Composition | http://www.petrolimex.com.vn/Desktop.aspx/Trang-Noi-Dung/Gia-co-so/ (In Vietnamese language) |
| Pump prices and margins | http://www.petrolimex.com.vn/Desktop.aspx/Trang-Noi-Dung/Gia-co-so/ (In Vietnamese language) |
Contact
Please find more information on GIZ International Fuel Price Database and http://www.giz.de/fuelprices



















