Difference between revisions of "Hydropower in Powering Agriculture"
***** (***** | *****) |
***** (***** | *****) |
||
| Line 20: | Line 20: | ||
<br/> | <br/> | ||
| + | |||
= System Example: Smart Hydropower (In-Stream Turbine) <br/> = | = System Example: Smart Hydropower (In-Stream Turbine) <br/> = | ||
| Line 29: | Line 30: | ||
<br/>Calculation for the power equation:<br/> | <br/>Calculation for the power equation:<br/> | ||
| − | <font | + | <font face="roboto-medium" size="2" color="#1a1921"><font face="roboto-medium" size="2" color="#1a1921"><font face="roboto-medium" size="2" color="#1a1921">P=ρ*q*g*h*η</font></font></font> |
| − | <font | + | <font face="roboto-regular" size="2" lang="ja" color="#1a1921"><font face="roboto-regular" size="2" lang="ja" color="#1a1921"><font face="roboto-regular" size="2" lang="ja" color="#1a1921">q= water flow rate [m3/s]</font></font></font> |
| − | <font | + | <font face="roboto-regular" size="2" lang="ja" color="#1a1921"><font face="roboto-regular" size="2" lang="ja" color="#1a1921"><font face="roboto-regular" size="2" lang="ja" color="#1a1921">h= head (falling height) [m]</font></font></font> |
| − | <font | + | <font face="roboto-regular" size="2" lang="ja" color="#1a1921"><font face="roboto-regular" size="2" lang="ja" color="#1a1921"><font face="roboto-regular" size="2" lang="ja" color="#1a1921">ρ= density of water</font></font></font> |
| − | <font | + | <font face="roboto-regular" size="2" lang="ja" color="#1a1921"><font face="roboto-regular" size="2" lang="ja" color="#1a1921"><font face="roboto-regular" size="2" lang="ja" color="#1a1921">(1000[kg/m3])</font></font></font> |
| − | <font | + | <font face="roboto-regular" size="2" lang="ja" color="#1a1921"><font face="roboto-regular" size="2" lang="ja" color="#1a1921"><font face="roboto-regular" size="2" lang="ja" color="#1a1921">g= 9.81 [m/s</font></font></font><font face="roboto-regular" size="1" lang="ja" color="#1a1921"><font face="roboto-regular" size="1" lang="ja" color="#1a1921"><font face="roboto-regular" size="1" lang="ja" color="#1a1921">2</font></font></font><font face="roboto-regular" size="2" lang="ja" color="#1a1921"><font face="roboto-regular" size="2" lang="ja" color="#1a1921"><font face="roboto-regular" size="2" lang="ja" color="#1a1921">]</font></font></font> |
| − | <font | + | <font face="roboto-regular" size="2" lang="ja" color="#1a1921"><font face="roboto-regular" size="2" lang="ja" color="#1a1921"><font face="roboto-regular" size="2" lang="ja" color="#1a1921">η= efficiency of the systems, usually</font></font></font><font face="roboto-regular" size="2" lang="ja" color="#1a1921"><font face="roboto-regular" size="2" lang="ja" color="#1a1921"><font face="roboto-regular" size="2" lang="ja" color="#1a1921">between 50% and 75% for</font></font></font><font face="roboto-regular" size="2" lang="ja" color="#1a1921"><font face="roboto-regular" size="2" lang="ja" color="#1a1921"><font face="roboto-regular" size="2" lang="ja" color="#1a1921">micro/small hydro</font></font></font><br/> |
| − | <br/><font | + | <br/><font face="roboto-regular" size="2" lang="ja" color="#1a1921"><font face="roboto-regular" size="2" lang="ja" color="#1a1921"><font face="roboto-regular" size="2" lang="ja" color="#1a1921">The theoretical power output of such a hydropower system can be</font></font></font><font face="roboto-regular" size="2" lang="ja" color="#1a1921"><font face="roboto-regular" size="2" lang="ja" color="#1a1921"><font face="roboto-regular" size="2" lang="ja" color="#1a1921">estimated by multiplying the water flow of the river by the height</font></font></font><font face="roboto-regular" size="2" lang="ja" color="#1a1921"><font face="roboto-regular" size="2" lang="ja" color="#1a1921"><font face="roboto-regular" size="2" lang="ja" color="#1a1921">difference from intake to the turbine, the system efficiency as well</font></font></font><font face="roboto-regular" size="2" lang="ja" color="#1a1921"><font face="roboto-regular" size="2" lang="ja" color="#1a1921"><font face="roboto-regular" size="2" lang="ja" color="#1a1921">as some constants (see the calculation). An annual or daily energy yield can be</font></font></font><font face="roboto-regular" size="2" lang="ja" color="#1a1921"><font face="roboto-regular" size="2" lang="ja" color="#1a1921"><font face="roboto-regular" size="2" lang="ja" color="#1a1921">estimated by further multiplying the power output by the number of</font></font></font><font face="roboto-regular" size="2" lang="ja" color="#1a1921"><font face="roboto-regular" size="2" lang="ja" color="#1a1921"><font face="roboto-regular" size="2" lang="ja" color="#1a1921">hours the system is running during this period.</font></font></font><font face="roboto-regular" size="2" lang="ja" color="#1a1921"><font face="roboto-regular" size="2" lang="ja" color="#1a1921"><font face="roboto-regular" size="2" lang="ja" color="#1a1921">An alternative solution is an in-stream turbine. However, this type</font></font></font><font face="roboto-regular" size="2" lang="ja" color="#1a1921"><font face="roboto-regular" size="2" lang="ja" color="#1a1921"><font face="roboto-regular" size="2" lang="ja" color="#1a1921">has not yet been commercially used in a wider scale.</font></font></font><br/> |
<br/> | <br/> | ||
| − | |||
| − | |||
Revision as of 08:19, 19 September 2016
Overview
Worldwide, hydropower is the most widely used renewable energy resource due to its significant advantages over other renewable resources: high energy density, low cost and reliability in particular. Hydropower plants are available from very small sizes of only few Kilowatts (kW) to multi-Gigawatts (GW). Small hydropower plants, generally in kW range, are used for rural electrification in many countries and have high potential to be integrated into the agriculture value chain in those locations.
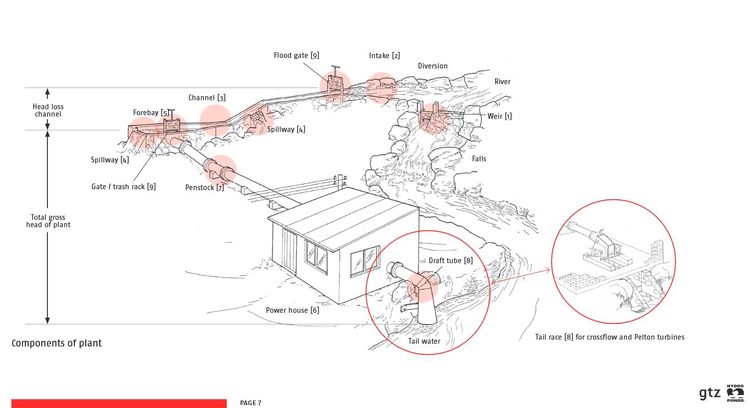
Hydropower, especially small-scale hydropower (up to 1 MW), works according to a simple principle: water from streams or rivers runs through a turbine, the turbine rotates and turns tools (pumps, mills etc.) or a generator which can produce electricity (see the figure below). To achieve a reliable production of energy, it is important to have good knowledge about the local water resources and to design the system accordingly.
|
|
► For more information see the Micro Hydro Power Scout Guide.
System Example: Smart Hydropower (In-Stream Turbine)
The Smart Hydropower turbine was developed to produce a maximum amount of electrical power with the kinetic energy of flowing waters. Because it is powered by kinetic energy and not with potential energy it is known as a so-called “zero-head” or “in-stream” turbine. As such, no dams and/or height differences are necessary for the operation of this device; the course of a river remains in its natural state and no high investments in infrastructure are required. Because the amount of kinetic energy (velocity) varies from river to river, the capacity of an in-stream turbine ranges: from a minimum of a few watts to a maximum of 5 kW.
Check out this video to learn more.
Calculation for the power equation:
P=ρ*q*g*h*η
q= water flow rate [m3/s]
h= head (falling height) [m]
ρ= density of water
(1000[kg/m3])
g= 9.81 [m/s2]
η= efficiency of the systems, usuallybetween 50% and 75% formicro/small hydro
The theoretical power output of such a hydropower system can beestimated by multiplying the water flow of the river by the heightdifference from intake to the turbine, the system efficiency as wellas some constants (see the calculation). An annual or daily energy yield can beestimated by further multiplying the power output by the number ofhours the system is running during this period.An alternative solution is an in-stream turbine. However, this typehas not yet been commercially used in a wider scale.
Further Information
- FAO Study: Opportunities for Agri-Food Chains to become Energy-Smart
- Reader of the MOOC "Powering Agriculture - Sustainable Energy for Food"
- Hydro Portal on energypedia
- Productive Use of Micro Hydro Power (MHP)
- Energypedia Portal of Powering Agriculture